Textbook Question
When designed matings cannot be conducted in an organism (for example, in humans), how do we learn that genes are linked, and how do we map them?
442
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


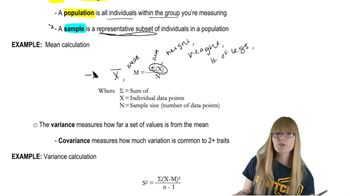
When designed matings cannot be conducted in an organism (for example, in humans), how do we learn that genes are linked, and how do we map them?
Write a short essay that discusses how crossing over can be detected and how the resultant data provide the basis of chromosome mapping.
Describe the cytological observation that suggests that crossing over occurs during the first meiotic prophase.
Explain why a 50 percent recovery of single-crossover products is the upper limit, even when crossing over always occurs between two linked genes?
Why are double-crossover events expected less frequently than single-crossover events?
What is the proposed basis for positive interference?