Textbook Question
How do we know that mutations occur randomly?
735
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

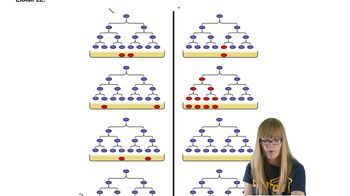

How do we know that mutations occur randomly?
How do we know that DNA repair mechanisms detect and correct the majority of spontaneous and induced mutations?
Write a short essay contrasting how these concepts may differ between bacteria and eukaryotes.
What is a spontaneous mutation, and why are spontaneous mutations rare?