An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by alternate segregation. Which, if any, of these gametes are viable?

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 10 - Eukaryotic Chromosome Abnormalities and Molecular Organization
Ch. 10 - Eukaryotic Chromosome Abnormalities and Molecular Organization Problem 13e
Problem 13e Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
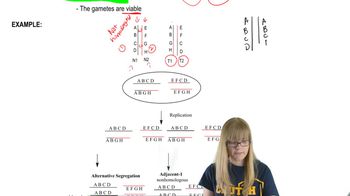

An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by alternate segregation. Which, if any, of these gametes are viable?
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by adjacent-1 segregation. Which, if any, of these gametes are viable?
An animal heterozygous for a reciprocal balanced translocation has the following chromosomes:
MN • OPQRST
MN • OPQRjkl
cdef • ghijkl
cdef • ghiST
Identify the gametes produced by adjacent-2 segregation. Which if any of these gametes are viable?
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis has an idea he thinks will be a boon to agriculture. He wants to create the 'pomato,' a hybrid between a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) that has 12 chromosomes and a potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 48 chromosomes. Dr. Dopsis is hoping his new pomato will have tuber growth like a potato and the fruit production of a tomato. He joins a haploid gamete from each species to form a hybrid and then induces doubling of chromosome number. How many chromosomes will the hybrid have before chromosome doubling?
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis has an idea he thinks will be a boon to agriculture. He wants to create the 'pomato,' a hybrid between a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) that has 12 chromosomes and a potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 48 chromosomes. Dr. Dopsis is hoping his new pomato will have tuber growth like a potato and the fruit production of a tomato. He joins a haploid gamete from each species to form a hybrid and then induces doubling of chromosome number. Will this hybrid be infertile?
Dr. Ara B. Dopsis has an idea he thinks will be a boon to agriculture. He wants to create the 'pomato,' a hybrid between a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) that has 12 chromosomes and a potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 48 chromosomes. Dr. Dopsis is hoping his new pomato will have tuber growth like a potato and the fruit production of a tomato. He joins a haploid gamete from each species to form a hybrid and then induces doubling of chromosome number.
How many chromosomes will the polyploid have after chromosome doubling?