List possible genotypes for lac operon haploids that have the following phenotypic characteristics:
The operon genes are constitutively transcribed, and the strain grows on lactose medium. List two possible genotypes for this phenotype.

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage
Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage Problem 21
Problem 21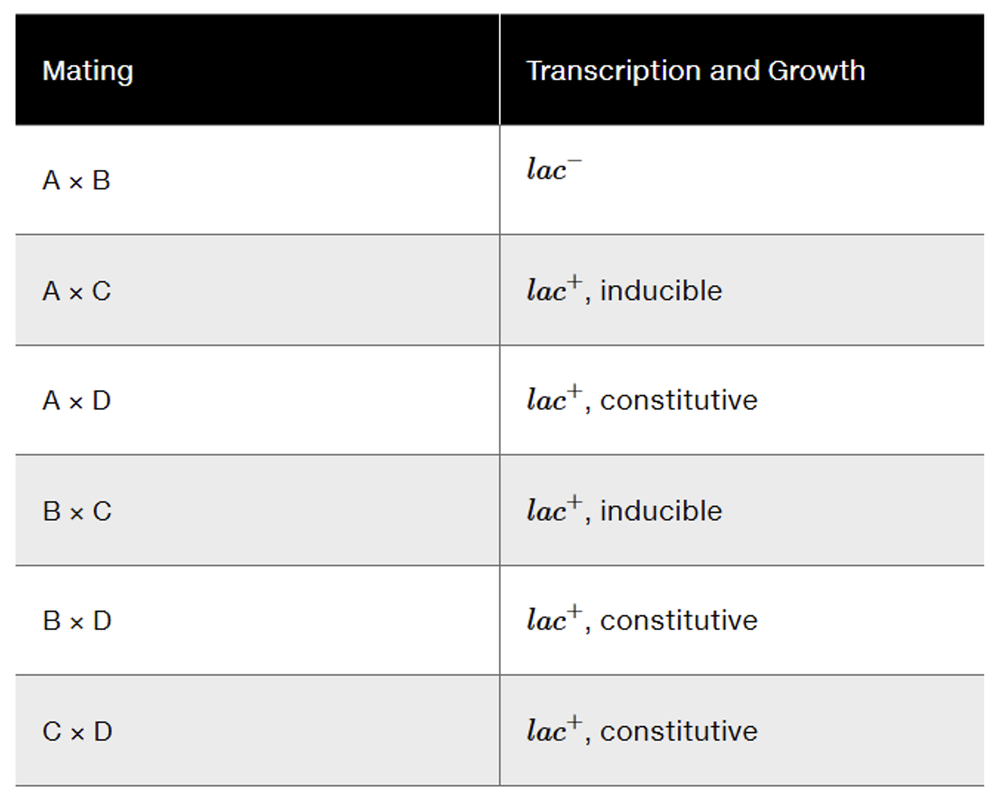
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



List possible genotypes for lac operon haploids that have the following phenotypic characteristics:
The operon genes are constitutively transcribed, and the strain grows on lactose medium. List two possible genotypes for this phenotype.
Suppose each of the genotypes you listed in parts (a) and (b) of Problem 19 are placed in a partial diploid genotype along with a chromosome that has a fully wild-type lac operon.
Will the transcription of operon genes in each partial diploid be inducible or constitutive?
Suppose each of the genotypes you listed in parts (a) and (b) of Problem 19 are placed in a partial diploid genotype along with a chromosome that has a fully wild-type lac operon.
Which partial diploids will be able to grow on a lactose medium?
Suppose the lac operon partial diploid cap⁻ I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁻ Y⁺/ cap⁺ I⁻ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁻ is grown.
Will this partial diploid strain grow on a lactose medium?
Suppose the lac operon partial diploid cap⁻ I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁻ Y⁺/ cap⁺ I⁻ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁻ is grown.
Is transcription of β-galactosidase and permease inducible, constitutive, or noninducible?
Suppose the lac operon partial diploid cap⁻ I⁺ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁻ Y⁺/ cap⁺ I⁻ P⁺ O⁺ Z⁺ Y⁻ is grown.
Explain how genetic complementation contributes to the growth habit of this strain.