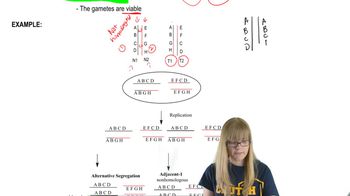
For the retinal cancer retinoblastoma, the inheritance of one mutated copy of RB1 from one of the parents is often referred to as a mutation that produces a 'dominant predisposition to cancer.' This means that the first mutation does not produce cancer but makes it very likely that cancer will develop.
Explain why cancer is almost certain to develop with the inheritance of one mutated copy of RB1.