Go to the website http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and enter 'Lynch syndrome' in the Search box at the top of the page. From the list of options given, select '#120435—Lynch Syndrome.' Use the information you retrieve to answer the following questions. What genes are most commonly mutated in Lynch syndrome?

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 14 - Analysis of Gene Function via Forward Genetics and Reverse Genetics
Ch. 14 - Analysis of Gene Function via Forward Genetics and Reverse Genetics Problem C.4b
Problem C.4bExplain the following processes involving chromosome mutations and cancer development.
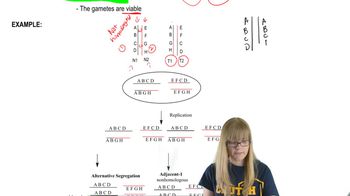
How the chromosome mutation producing Burkitt lymphoma generates the disease.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Chromosome Mutations

Burkitt Lymphoma and Chromosomal Translocation
Oncogenes and Cancer Development

Go to the website http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and enter 'Lynch syndrome' in the Search box at the top of the page. From the list of options given, select '#120435—Lynch Syndrome.' Use the information you retrieve to answer the following questions. Provide a brief summary of the normal functions of the protein products of these genes.
Go to the website http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and enter 'Lynch syndrome' in the Search box at the top of the page. From the list of options given, select '#120435—Lynch Syndrome.' Use the information you retrieve to answer the following questions. What are the approximate rates of cancer that develop in people carrying a mutation of one of these genes?
Go to the website http://www.cancer.gov and select 'Cancer Types' on the top menu bar. Scroll down to 'Breast Cancer' and click. Select 'Cases & Prevention' from the options. Click 'More information' and select 'BRCA Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing'. Use the information on this page to answer the following questions. Are there measures a woman with a positive result can take to lessen her chances of developing cancer or to catch a cancer early in its development?
Based on what you read in this chapter, Can a tumor arise from a single mutated cell? Are all the cells in a tumor identical?
Why do most cancers require the mutation of multiple genes?