In selective breeding experiments, it is frequently observed that the strains respond to artificial selection for many generations, with the selected phenotype changing in the desired direction. Often, however, the response to artificial selection reaches a plateau after many generations, and the phenotype no longer changes as it did in past generations. Once a plateau has been reached, is the heritability of the trait very high or is it very low? Explain.

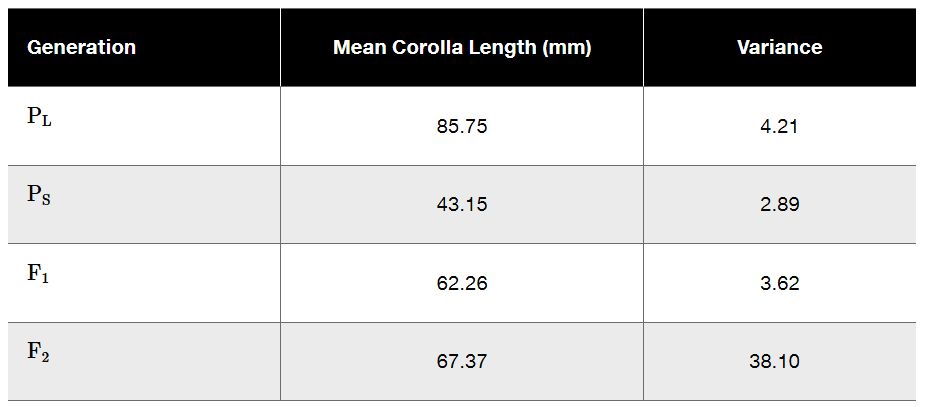
In Nicotiana, two inbred strains produce long (PL) and short (PS) corollas. These lines are crossed to produce F₁, and the F₁ are crossed to produce F₂ plants in which corolla length and variance are measured. The following table summarizes the mean and variance of corolla length in each generation. Calculate H² for corolla length in Nicotiana.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Heritability (H²)

Phenotypic Variance (Vp)

Genetic Variance (Vg)

Two inbred lines of sunflowers (P₁ and P₂) produce different total weights of seeds per flower head. The mean weight of seeds (grams) and the variance of seed weights in different generations are as follows:
Use the information above to determine VG, VE, and VP for this trait.
What is a quantitative trait locus (QTL)? Suppose you wanted to search for QTLs influencing fruit size in tomatoes. Describe the general structure of a QTL experiment, including the kind of tomato strains you would use, how molecular markers should be distributed in the genome, how the genetic marker alleles should differ between the two strains, and how you would use the F₁ progeny in a subsequent cross to obtain information about the possible location(s) of QTLs of interest.
Suppose the length of maize ears has narrow sense heritability (h²) of 0.70. A population produces ears that have an average length of 28 cm, and from this population a breeder selects a plant producing 34-cm ears to cross by self-fertilization. Predict the selection differential (S) and the response to selection (R) for this cross.
In a line of cherry tomatoes, the average fruit weight is 16 g. A plant producing tomatoes with an average weight of 12 g is used in one self-fertilization cross to produce a line of smaller tomatoes, and a plant producing tomatoes of 24 g is used in a second cross to produce larger tomatoes. What is the selection differential (S) for fruit weight in each cross?
In a line of cherry tomatoes, the average fruit weight is 16 g. A plant producing tomatoes with an average weight of 12 g is used in one self-fertilization cross to produce a line of smaller tomatoes, and a plant producing tomatoes of 24 g is used in a second cross to produce larger tomatoes. If narrow sense heritability (h²) for this trait is 0.80, what are the expected responses to selection (R) for fruit weight in the crosses?
