In a line of cherry tomatoes, the average fruit weight is 16 g. A plant producing tomatoes with an average weight of 12 g is used in one self-fertilization cross to produce a line of smaller tomatoes, and a plant producing tomatoes of 24 g is used in a second cross to produce larger tomatoes. If narrow sense heritability (h²) for this trait is 0.80, what are the expected responses to selection (R) for fruit weight in the crosses?

Two pure-breeding wheat strains, one producing dark red kernels and the other producing white kernels, are crossed to produce F₁ with pink kernel color. When an F₁ plant is self-fertilized and its seed collected and planted, the resulting F₂ consists of 160 plants with kernel colors as shown in the following table.
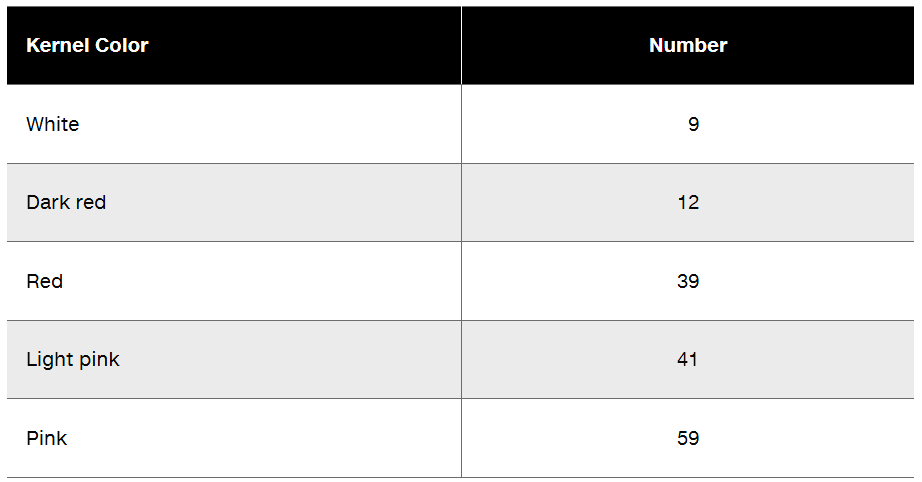
Using clearly defined allele symbols of your choice, give genotypes for the parental strains and the F₁. Describe the genotypes that produce the different phenotypes in the F₂.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Mendelian Genetics

Alleles and Genotypes

Phenotypic Ratios

Two pure-breeding wheat strains, one producing dark red kernels and the other producing white kernels, are crossed to produce F₁ with pink kernel color. When an F₁ plant is self-fertilized and its seed collected and planted, the resulting F₂ consists of 160 plants with kernel colors as shown in the following table.
Based on the F₂ progeny, how many genes are involved in kernel color determination?
Two pure-breeding wheat strains, one producing dark red kernels and the other producing white kernels, are crossed to produce F₁ with pink kernel color. When an F₁ plant is self-fertilized and its seed collected and planted, the resulting F₂ consists of 160 plants with kernel colors as shown in the following table.
How many additive alleles are required to explain the five phenotypes seen in the F₂?
Two pure-breeding wheat strains, one producing dark red kernels and the other producing white kernels, are crossed to produce F₁ with pink kernel color. When an F₁ plant is self-fertilized and its seed collected and planted, the resulting F₂ consists of 160 plants with kernel colors as shown in the following table.
If an F₁ plant is crossed to a dark red plant, what are the expected progeny phenotypes, and what is the expected proportion of each phenotype?
In studies of human MZ and DZ twin pairs of the same sex who are reared together, the following concordance values are identified for various traits. Based on the values shown, describe the relative importance of genes versus the influence of environmental factors for each trait.
During a visit, your grandparents comment on how tall you are compared with them. You tell them that in your genetics class, you learned that height in humans has high heritability, although environmental factors also influence adult height. You correctly explain the meaning of heritability, and your grandfather asks, 'How can height be highly heritable and still be influenced by the environment?' What explanation do you give your grandfather?
