Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected proportions of the following progeny?
A phenotype identical to either parent

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected proportions of the following progeny?
A phenotype identical to either parent
Organisms with the genotypes AABbCcDd and AaBbCcDd are crossed. What are the expected proportions of the following progeny?
A–B–ccdd
Blue moon beans produce beans that are either the dominant color blue or the recessive color white. The bean pods for this species always contain four seeds each. If two heterozygous plants that each have the Bb genotype are crossed, what are the predicted frequencies of each of the five outcome classes for combinations of blue and white seeds in pods?
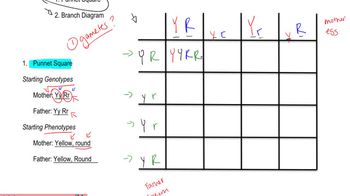
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. The three genes have dominant and recessive alleles, with tall (T) dominant to short (t), round (R) dominant to wrinkled (r), and yellow (G) dominant to green (g).
If a true-breeding tall, wrinkled, yellow plant is crossed to a true-breeding short, round, green plant, what phenotypic ratios are expected in the F1 and F2?
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. The three genes have dominant and recessive alleles, with tall (T) dominant to short (t), round (R) dominant to wrinkled (r), and yellow (G) dominant to green (g).
What proportion of the F2 are expected to be tall, wrinkled, yellow? ttRRGg?
In pea plants, plant height, seed shape, and seed color are governed by three independently assorting genes. The three genes have dominant and recessive alleles, with tall (T) dominant to short (t), round (R) dominant to wrinkled (r), and yellow (G) dominant to green (g).
What proportion of the that produce round, green seeds (regardless of the height of the plant) are expected to breed true?