Why might mitochondrial, Y chromosome, and autosomal DNA provide different perspectives on our evolutionary past, for example, with respect to our relationship with Neanderthals?
Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels

Sanders3rd EditionGenetic Analysis: An Integrated ApproachISBN: 9780135564172Not the one you use?Change textbook
All textbooks Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels
Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels Problem D.4
Problem D.4
 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels
Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels Problem D.4
Problem D.4Chapter 20, Problem D.4
Discuss how both gains and losses of regulatory elements may lead to human-specific traits.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by defining regulatory elements in genetics: these are DNA sequences such as enhancers, silencers, promoters, and insulators that control the expression of genes without altering the protein-coding sequence itself.
Explain that gains of regulatory elements refer to the acquisition of new regulatory sequences or the modification of existing ones, which can lead to novel patterns of gene expression unique to humans, potentially contributing to human-specific traits.
Discuss how losses of regulatory elements involve the deletion or inactivation of certain regulatory sequences, which can reduce or eliminate gene expression in specific contexts, also resulting in traits that distinguish humans from other species.
Illustrate with examples how changes in regulatory elements can affect developmental pathways, brain function, or other physiological processes, emphasizing that these changes can be subtle but have significant phenotypic effects.
Conclude by highlighting that both gains and losses of regulatory elements contribute to evolutionary divergence by altering gene expression patterns, thereby shaping human-specific traits without changing the underlying protein-coding genes.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Regulatory Elements in Genetics
Regulatory elements are DNA sequences such as enhancers, silencers, and promoters that control gene expression levels. They do not code for proteins but influence when, where, and how much a gene is expressed, playing a crucial role in development and phenotype.
Recommended video:
Guided course
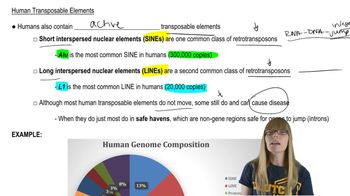
Human Transposable Elements
Gene Expression and Phenotypic Variation
Changes in gene expression, driven by regulatory elements, can lead to differences in traits without altering the underlying protein-coding genes. Variations in expression patterns contribute to phenotypic diversity, including species-specific characteristics.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Penetrance and Expressivity
Evolutionary Impact of Gains and Losses of Regulatory Elements
Gains (e.g., new enhancers) or losses (e.g., deletion of silencers) of regulatory elements can modify gene expression patterns, leading to novel traits or loss of ancestral traits. Such changes are key mechanisms in human evolution, contributing to traits unique to our species.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Transposable Elements
Related Practice
Textbook Question
689
views
Textbook Question
What insights have analyses of human mitochondrial DNA provided into our recent evolutionary past?
873
views
Textbook Question
What lines of evidence support the hypothesis that modern humans evolved in Africa and then subsequently migrated throughout the globe?
574
views
Textbook Question
Carl Linnaeus, the 18th-century botanist who laid the foundation for the modern system of taxonomic nomenclature, placed chimpanzees and humans in the same genus. Discuss the merits of this classification.
700
views
Textbook Question
How do copy-number variants arise? Do they account for more polymorphism than SNPs within the human population?
511
views
Textbook Question
Consider possible societal and ethical dilemmas that might arise if we currently shared the planet with another hominin.
527
views