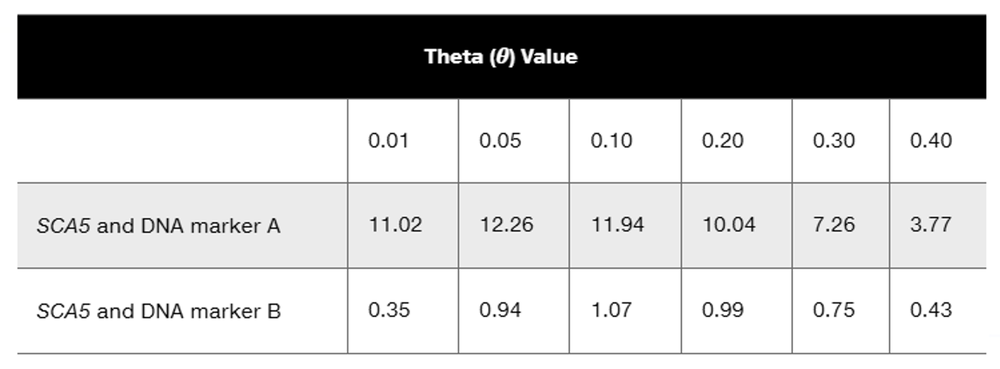
A 2006 genetic study of a large American family (Ikeda et al., 2006) identified genetic linkage between DNA markers on chromosome 11 and the gene producing the autosomal dominant neuromuscular disorder spinocerebellar ataxia type 5 (SCA5). The following lod score data are taken from the 2006 study:
Does either group of lod scores indicate statistically significant odds in favor of genetic linkage? Explain your answer.