DNA sequences for 10 individuals are
How many different SNP haplotypes are represented in the data?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



DNA sequences for 10 individuals are
How many different SNP haplotypes are represented in the data?
DNA sequences for 10 individuals are
What is the sequence of each haplotype?
DNA sequences for 10 individuals are
Identify the haplotype carried by each person.
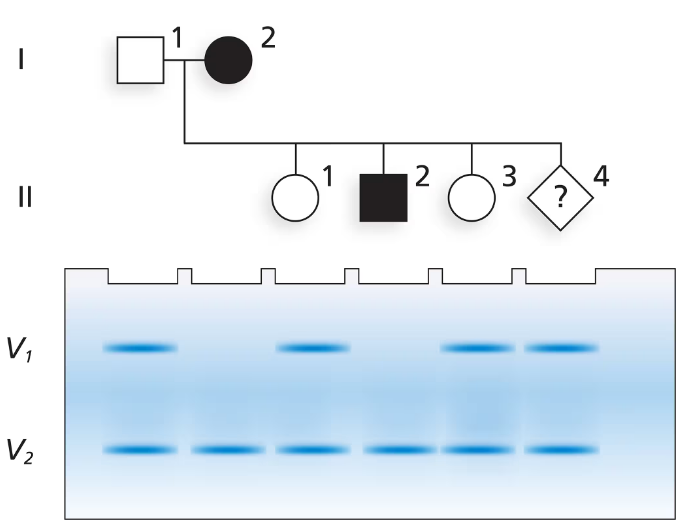
The accompanying pedigree below shows a family in which an autosomal recessive disorder is present. Family members I-2 and II-2 are affected by the disorder and have the genotype dd. A pregnancy involving II-4 has just undergone genetic testing for a VNTR that is linked to the disease gene. The VNTR has a recombination frequency of r = 20 with the disease gene. The VNTR has two alleles, V1 and V2. The gel electrophoresis patterns for each family member are shown, including the VNTR genotype for II-4. Based on the information given, answer the following questions about the family.
What is the genotype of each family member, including II-4, for the VNTR?
The accompanying pedigree below shows a family in which an autosomal recessive disorder is present. Family members I-2 and II-2 are affected by the disorder and have the genotype dd. A pregnancy involving II-4 has just undergone genetic testing for a VNTR that is linked to the disease gene. The VNTR has a recombination frequency of r = 20 with the disease gene. The VNTR has two alleles, V1 and V2. The gel electrophoresis patterns for each family member are shown, including the VNTR genotype for II-4. Based on the information given, answer the following questions about the family.
What are the syntenic disease gene and VNTR alleles in I-1 and I-2?
The accompanying pedigree below shows a family in which an autosomal recessive disorder is present. Family members I-2 and II-2 are affected by the disorder and have the genotype dd. A pregnancy involving II-4 has just undergone genetic testing for a VNTR that is linked to the disease gene. The VNTR has a recombination frequency of r = 20 with the disease gene. The VNTR has two alleles, V1 and V2. The gel electrophoresis patterns for each family member are shown, including the VNTR genotype for II-4. Based on the information given, answer the following questions about the family.
What is the chance II-4 has the disease?