The principles of complementary base pairing and antiparallel polarity of nucleic acid strands in a duplex are universal for the formation of nucleic acid duplexes. What is the chemical basis for this universality?

The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
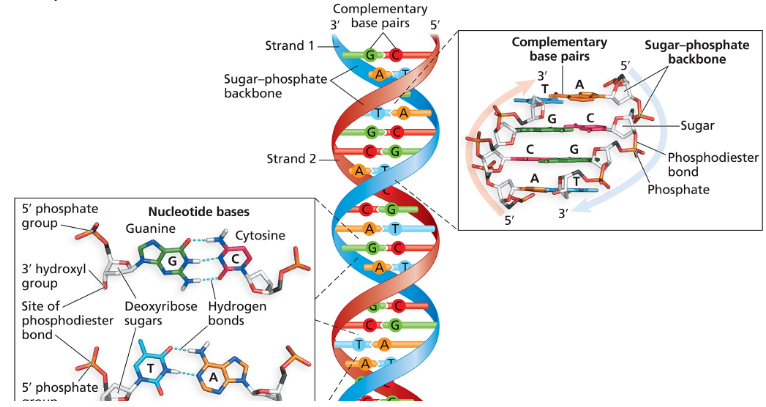
What kind of bonds join the C in one strand to the G in the complementary strand?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Nucleotides

Complementary Base Pairing

Hydrogen Bonds

For the following fragment of DNA, determine the number of hydrogen bonds and the number of phosphodiester bonds present:
5'-ACGTAGAGTGCTC-3'
3'-TGCATCTCACGAG-5'
The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
What kind of bond joins the C to G within a single strand?
The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
How many phosphodiester bonds are present in this DNA duplex?
The following figure (Figure 1.6) presents simplified depictions of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, a nucleotide base, and a phosphate group. Use this simplified method of representation to illustrate the sequence 3'-AGTCGAT-5' and its complementary partner in a DNA duplex.
How many hydrogen bonds are present in this DNA duplex?
Consider the sequence 3'-ACGCTACGTC-5'.
What is the double-stranded sequence?
