Which of the following equalities is not true for double-stranded DNA?
(G+A)=(C+T)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Which of the following equalities is not true for double-stranded DNA?
(G+A)=(C+T)
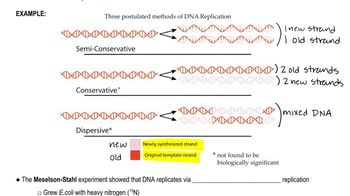
List the order in which the following proteins and enzymes are active in E. coli DNA replication: DNA pol I, SSB, ligase, helicase, DNA pol III, and primase.
Two viral genomes are sequenced, and the following percentages of nucleotides are identified:
Genome 1: A=28%, C=22%,G=28%,T=22%
Genome 2: A=22%, C=28%,G=28%,T=22%
Are the DNA molecules in each genome single-stranded or double-stranded?
Raymond Rodriguez and colleagues demonstrated conclusively that DNA replication in E. coli is bidirectional. Explain why locating the origin of replication on one side of the circular chromosomes and the terminus of replication on the opposite side of the chromosome supported this conclusion.
Joel Huberman and Arthur Riggs used pulse–chase labeling to examine the replication of DNA in mammalian cells. Briefly describe the Huberman–Riggs experiment, and identify how the results exclude a unidirectional model of DNA replication.
Why do the genomes of eukaryotes, such as Drosophila, need to have multiple origins of replication, whereas bacterial genomes, such as that of E. coli, have only a single origin?