Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
Ribosomal RNA is not processed.

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 8 - Molecular Biology of Transcription and RNA Processing
Ch. 8 - Molecular Biology of Transcription and RNA Processing Problem 29c
Problem 29c Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
Ribosomal RNA is not processed.
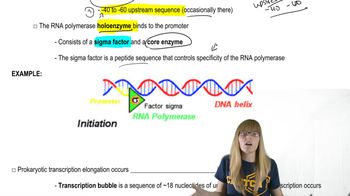
The DNA sequence below gives the first 12 base pairs of the transcribed region of a gene, and the template and nontemplate strands of DNA are identified. The transcription start is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the sequence given. Use the diagram to answer the list of questions. Make a copy of the diagram before you begin answering the questions, or have one group member diagram the answers for bacteria and another group member diagram the answers for eukaryotes.
Nontemplate strand ___________ TTGCTACGGTCA___________
Template strand ___________ AACGATGCCAGT___________
Write the polarity of the two DNA strands shown.
The DNA sequence below gives the first 12 base pairs of the transcribed region of a gene, and the template and nontemplate strands of DNA are identified. The transcription start is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the sequence given. Use the diagram to answer the list of questions. Make a copy of the diagram before you begin answering the questions, or have one group member diagram the answers for bacteria and another group member diagram the answers for eukaryotes.
Nontemplate strand ___________ TTGCTACGGTCA___________
Template strand ___________ AACGATGCCAGT___________
Give the mRNA transcript sequence and the polarity of the transcript.
The DNA sequence below gives the first 12 base pairs of the transcribed region of a gene, and the template and nontemplate strands of DNA are identified. The transcription start is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the sequence given. Use the diagram to answer the list of questions. Make a copy of the diagram before you begin answering the questions, or have one group member diagram the answers for bacteria and another group member diagram the answers for eukaryotes. Nontemplate strand ___________TTGCTACGGTCA___________
Template strand ___________ AACGATGCCAGT___________
Assuming the sequence shown is part of a bacterial gene, what consensus sequence(s) would you expect to identify in the promoter?
The DNA sequence below gives the first 12 base pairs of the transcribed region of a gene, and the template and nontemplate strands of DNA are identified. The transcription start is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the sequence given. Use the diagram to answer the list of questions. Make a copy of the diagram before you begin answering the questions, or have one group member diagram the answers for bacteria and another group member diagram the answers for eukaryotes. Nontemplate strand ___________TTGCTACGGTCA___________
Template strand ___________AACGATGCCAGT___________
Write the anticipated bacterial consensus sequence(s) in the approximate position(s) on the diagram.
The DNA sequence below gives the first 12 base pairs of the transcribed region of a gene, and the template and nontemplate strands of DNA are identified. The transcription start is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the sequence given. Use the diagram to answer the list of questions. Make a copy of the diagram before you begin answering the questions, or have one group member diagram the answers for bacteria and another group member diagram the answers for eukaryotes.
Nontemplate strand ___________ TTGCTACGGTCA___________
Template strand ___________ AACGATGCCAGT___________
Assuming the sequence shown is part of a eukaryotic gene, what consensus sequence(s) would you expect to identify within about 100 base pairs of the start of transcription?