Textbook Question
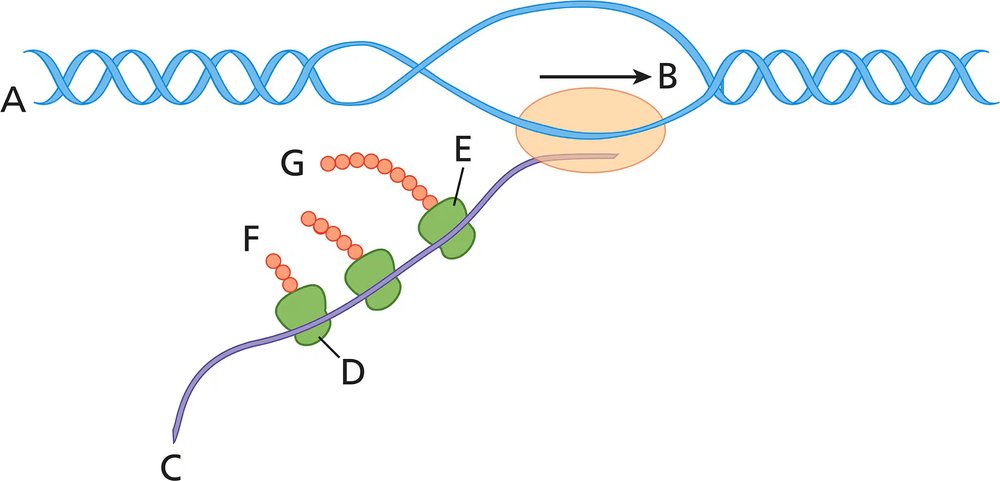
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Which end of the DNA is closest to A?
619
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Which end of the DNA is closest to A?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to B?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What is the name of the molecule closest to C?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to D? Be specific.
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to E? Be specific.
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What name is given to the object looking like a string of beads that is closest to F?