Textbook Question
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
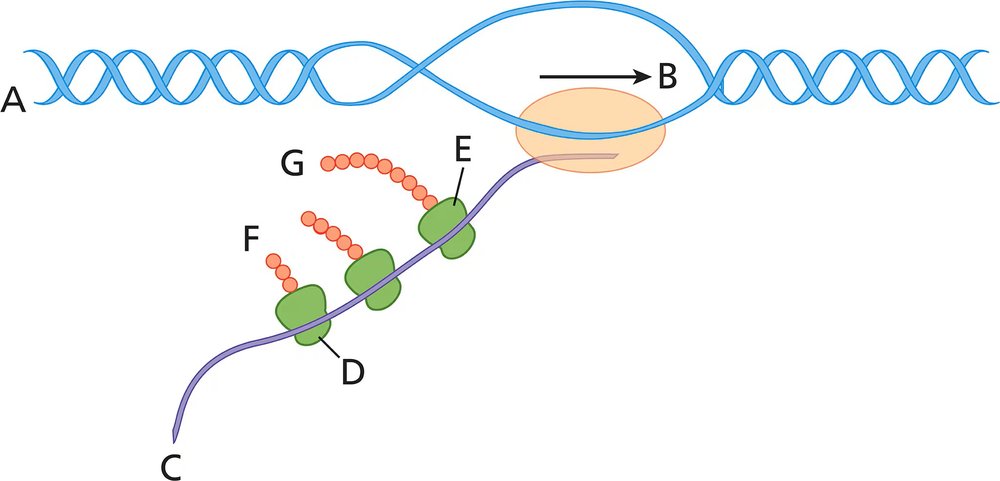
Which end of the molecule is closest to C?
504
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Which end of the molecule is closest to C?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to D? Be specific.
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to E? Be specific.
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Indicate where fMet is located in the string to the right of G.
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Which end of the polypeptide is closest to G?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What process(es) are illustrated in the diagram?