Organisms of all three domains of life usually use the mRNA codon AUG as the start codon.
Do organisms of the three domains use the same amino acid as the initial amino acid in translation? Identify similarities and differences.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Organisms of all three domains of life usually use the mRNA codon AUG as the start codon.
Do organisms of the three domains use the same amino acid as the initial amino acid in translation? Identify similarities and differences.
Organisms of all three domains of life usually use the mRNA codon AUG as the start codon.
Despite AUG being the most common start codon sequence, very few proteins have methionine as the first amino acid. Why is this the case?
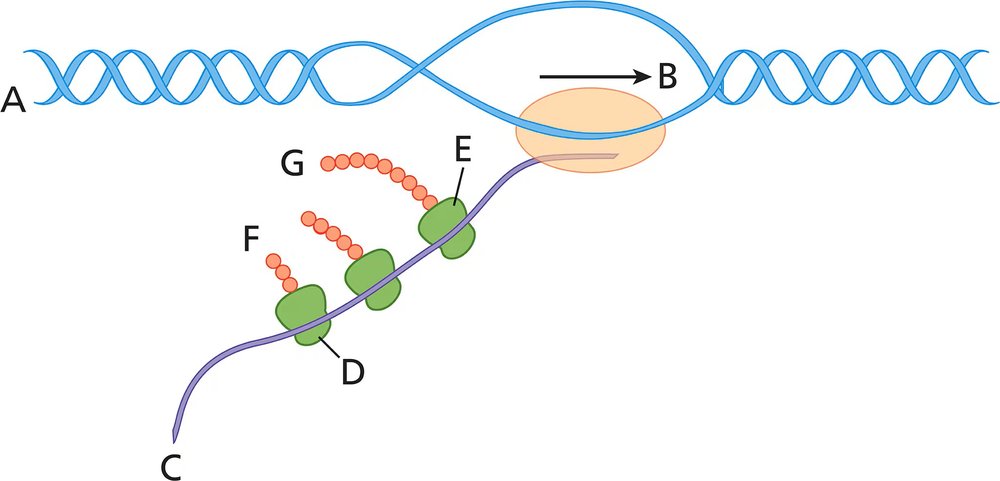
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Is the DNA nearest A the template strand or the coding strand?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to B?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What is the name of the molecule closest to C?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Which end of the molecule is closest to C?