Textbook Question
Name the electron carrier that transports electrons from complex I to complex III.
1478
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
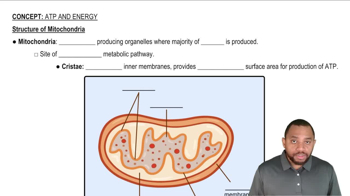
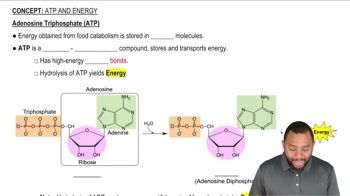
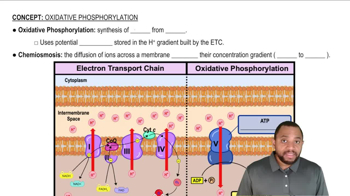
Name the electron carrier that transports electrons from complex I to complex III.
Name the complex where FADH2 enters electron transport.
According to the chemiosmotic theory, how does the proton gradient provide energy to synthesize ATP?
List the energy yield in ATP molecules for each of the following:
a. NADH → NAD+
List the energy yield in ATP molecules for each of the following:
c. 2 Pyruvate → 2 acetyl CoA + 2 CO2
List the energy yield in ATP molecules for each of the following:
a. FADH2 → FAD