Textbook Question
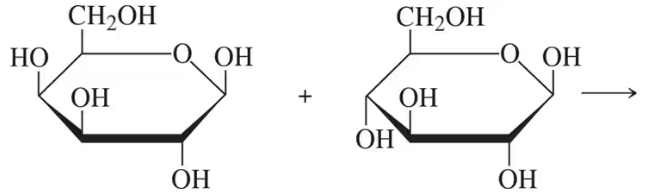
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of reduction reaction of D-galactose at C1.
762
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Draw the Fischer projection of the product of reduction reaction of D-galactose at C1.
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict's test?
a. D-glucose
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict’s test?
b. lactose
Isomaltose, a disaccharide formed during caramelization in cooking, contains two glucose units bonded ⍺(1→6). Draw the structure of isomaltose.
The glycosidic bond in a disaccharide was determined to be α(1→6). Hydrolysis of the disaccharide produced one galactose and one fructose. Draw the structure of the disaccharide.
Our bodies cannot digest cellulose because we lack the enzyme cellulase. Why is cellulose an important part of a healthy diet if we cannot digest it?