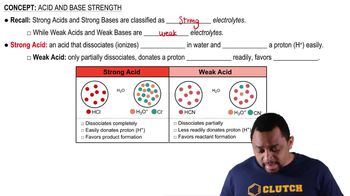
Cobalt(II) chloride, a blue solid, can absorb water from the air to form cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate, a pink solid. The equilibrium is so sensitive to moisture in the air that CoCl2 is used as a humidity indicator.
a. Write a balanced equation for the equilibrium. Be sure to include water as a reactant to produce the hexahydrate.