A typical oral rehydration solution (ORS) for infants contains 90 mEq/L Na+ , 20 mEq/L K+ , 110 mEq/L Cl- , and 2.0% (m/v) glucose (MW = 180g/mol)
a. Calculate the concentration of each ORS component in units of molarity.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


A typical oral rehydration solution (ORS) for infants contains 90 mEq/L Na+ , 20 mEq/L K+ , 110 mEq/L Cl- , and 2.0% (m/v) glucose (MW = 180g/mol)
a. Calculate the concentration of each ORS component in units of molarity.
A typical oral rehydration solution (ORS) for infants contains 90 mEq/L Na+, 20 mEq/L K+, 110 mEq/L Cl– and 2.0% (m/v) glucose (MW = 180g/mol).
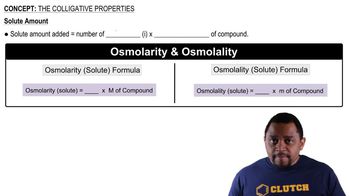
b. What is the osmolarity of the solution, and how does it compare with the osmolarity of blood plasma?
Assume that two liquids are separated by a semipermeable membrane, with pure solvent on the right side and a solution of a solute on the left side. Make a drawing that shows the situation after equilibrium is reached.
<IMAGE>
HF is a weak electrolyte and HBr is a strong electrolyte. Which of the curves in the figure represents the change in the boiling point of an aqueous solution when 1 mole of HF is added to 1 kg of water, and which represents the change when 1 mol of HBr is added?
<IMAGE>
How can you tell a solution from a colloid?
Why does water not dissolve motor oil?