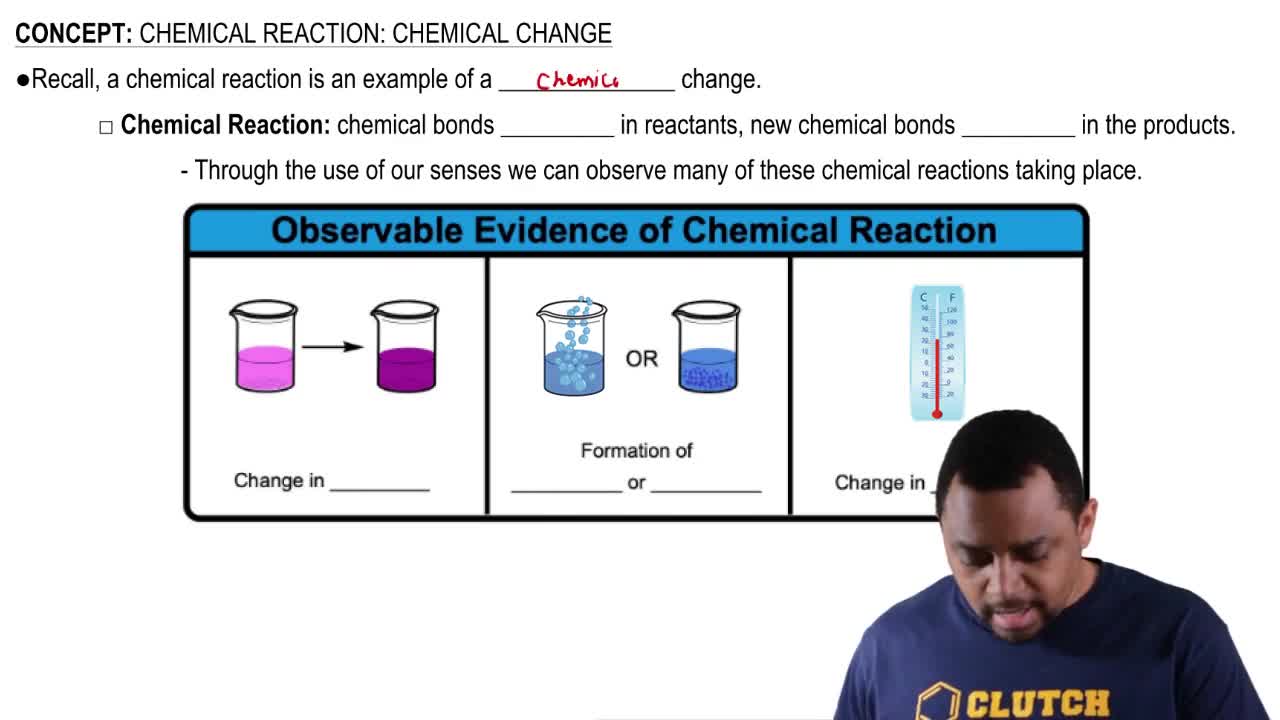
Textbook Question
Write the names for the elements in each of the following formulas of compounds used in medicine:
c. Demerol, C15H22ClNO2
1316
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Write the names for the elements in each of the following formulas of compounds used in medicine:
c. Demerol, C15H22ClNO2
Identify the group or period number described by each of the following:
a. contains C, N, and O
Identify the group or period number described by each of the following:
b. begins with helium
Give the symbol of the element described by each of the following:
a. the alkaline earth metal in Period 2