Back
BackProblem 1
List three features of the genetic code.
Problem 2
Indicate the true statements and then correct the false statements so that they are true.
a. DNA is replicated in a 3' to 5' direction.
b. DNA has a parallel arrangement.
c. RNA primase is required on the leading and the lagging strand.
d. DNA ligase forms phosphodiester bonds between Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
e. Prokaryotic mRNA requires processing before it is translated.
f. In RNA, A bonds to U.
g. In DNA, C bonds with G.
h. RNA contains deoxyribonucleotides.
Problem 3
Select the false statement:
a. DNA is made of deoxyribonucleotides.
b. RNA is made of ribonucleotides.
c. RNA is built in a 5' to 3' direction.
d. DNA is built in a 5' to 3' direction.
e. RNA primase builds RNA in transcription.
Problem 5
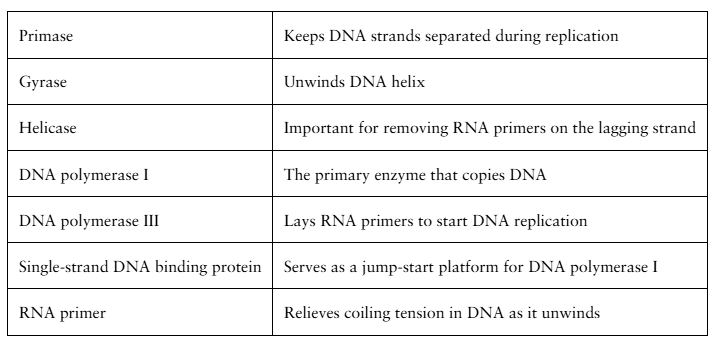
Match the following:
Problem 5.4
During ___________ a pilus forms between an F+ and an F−cell and allows for the exchange of genetic material. By the end of the process, the previously F− cell is converted to a(n) ___________ cell.
Problem 6
Codons are ___________ nucleotides long and are in ___________, which is transcribed from DNA. During ___________, tRNAs serve as adapter molecules to bring ___________ to the ribosome to build a protein. Once the ribosome reaches a(n) ___________ on the mRNA, translation ends.
Problem 7
Assume you have the DNA sequence 3'-ACGTATCCAGCAGCTCCACCAA-5'.
Use the genetic code table found in the chapter to answer the following questions:
a. What would the complementary DNA sequence be?
b. What would the corresponding mRNA sequence be?
c. Could the mRNA sequence you generated be translated? Why or why not?
Problem 8
Label the following as a biological, chemical, or physical mutagen:
UV radiation:
Transposons:
Cigarette smoke:
Viruses:
X-rays:
Plasmids:
Alcohol:
Problem 9
How is a ribonucleotide different from a deoxyribonucleotide?
Problem 10
For the lactose operon to be “on” and actively transcribed, ___________ must be present and ___________ must be absent.
Problem 11
Why are the terms gene expression and protein synthesis often used interchangeably?
Problem 12
What would the likely consequence be if a gene’s promoter was deleted or severely mutated?
Problem 13
Which of the following are involved in pre-transcriptional regulation? Select all that apply.
a. Methylation
b. Riboswitches
c. Operons
d. Short interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
e. Transcription factors
Problem 14
In eukaryotic cells, mRNA must be ___________ before it is ___________ into protein. In this process ___________ sequences are removed from the mRNA and ___________ are joined. A complex called the ___________ performs this process.
Problem 15
Does the statement apply to DNA, RNA, or both?
a. Contains uracil
b. Usually double stranded
c. Found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
d. Contains thymine
e. Is made by transcription
f. Contains adenine
g. Made of nucleotides
h. Contains ribose
i. Contains phosphodiester bonds
j. Built in a 5' to 3' direction
Problem 16
Classify the effects of the following mutations as missense, nonsense, or silent (use the genetic code table in the chapter to help you):
a. mRNA codon AUG is mutated to AUC
b. mRNA codon UAC is mutated to UAA
c. mRNA codon GGC is mutated to GGG
d. mRNA codon UAA is mutated to UAG
e. mRNA codon UGG is mutated to CGA
Problem 17
Which of the following helps to prevent mutations? Select all that apply.
a. Conjugation
b. Transposons
c. Transduction
d. DNA proofreading
e. Specialized transduction
f. Excision repair
Problem 18
Select all the true statements about repressible operons:
a. By default they are on until turned off.
b. An example is the lactose operon.
c. An example is the arginine operon.
d. A repressor must bind to the operator in order for the operon to be turned off.
Problem 19
Quorum sensing helps cells _______.
a. mutate
b. form biofilms
c. carry out transduction
d. copy their DNA
e. perform conjugation
Problem 20
Cells that can be transformed are said to be ___________.
Problem 21
In Griffith's classical experiments on transformation, which of the following scenarios led to a dead mouse? Select all that apply.
a. Infecting the mouse with a living strain of S. pneumoniae that makes a capsule
b. Infecting the mouse with a heat-killed strain of S. pneumoniae that makes a capsule
c. Infecting the mouse with a heat-killed strain of S. pneumoniae that makes a capsule and a living strain of S. pneumoniae that cannot make a capsule
d. Infecting the mouse with a living strain of S. pneumoniae that cannot make a capsule
Problem 22
Protein synthesis occurs in two main stages: ___________ and ___________.
Problem 23
Which of the following is produced by transcription?
a. mRNA
b. Protein
c. DNA
d. None of the above
Problem 24
Use the genetic code table in the chapter and the DNA sequence below to answer the following questions:
3'-TACATAAAATAATGGCGTTCTATT-5'
a. What would the mRNA sequence be, based on the provided DNA sequence?
b. What would the corresponding polypeptide sequence be for this DNA sequence?
c. What tRNA anticodon loop would correspond to the third codon of the mRNA?
d. What would the mRNA and polypeptide sequences be if the second adenine in the DNA was deleted?
Problem 25
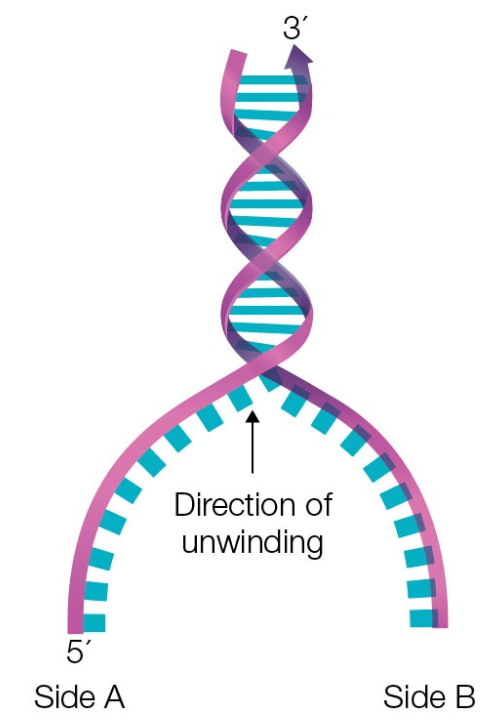
The following is a schematic of the parent DNA that is about to be replicated. Which side of the pictured DNA molecule (A or B) would be the leading side? Explain your answer.