Join instructor Cathy Evins to hear how flipping her class made her class time more effective and improved course outcomes.
Liberal Arts Math & Quantitative Reasoning
Support your students’ learning with these resources

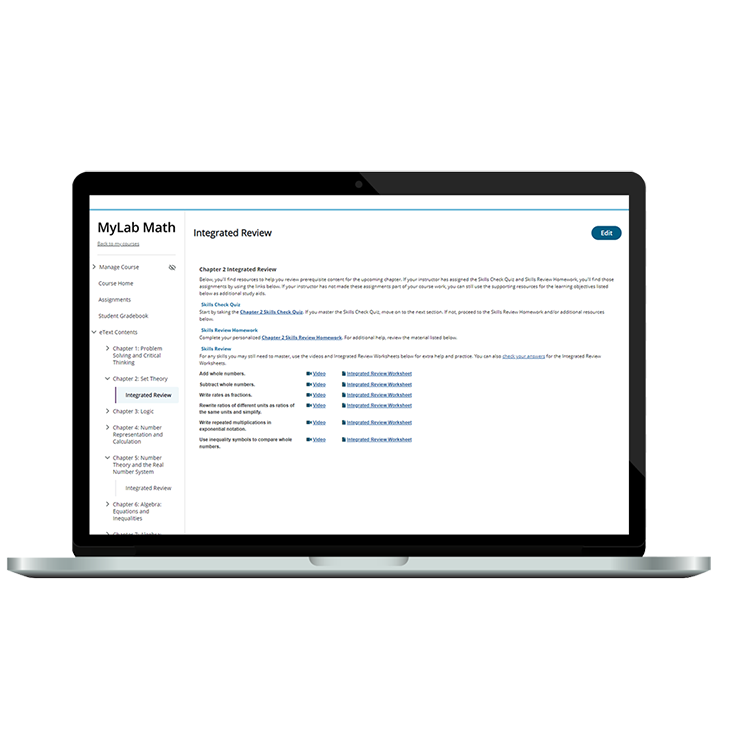
MyLab
MyLab® gives you the tools to easily customize your course and guide students to real results.

Pearson+
Pearson+ empowers students to choose how they learn best with easy-to-use eTextbooks and study tools.

AI-Powered Study Tool
Our AI-powered study tool transforms mistakes into teachable moments, helping students build confidence and study smarter.





Explore titles for liberal arts math and quantitative reasoning.
Join Aaron Warnock, Faculty Advisor at Pearson, to learn why Learning Catalytics can become an effective student engagement tool in your MyLab® courses.
Join Dr. Jeffrey Bennett for a strategy discussion, featuring examples for improving our teaching success at almost any level of math and statistics.