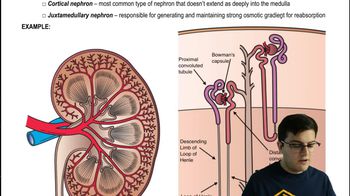
Unlike an earthworm's metanephridia, a mammalian nephron
a. Is intimately associated with a capillary network.
b. Functions in both osmoregulation and excretion.
c. Receives filtrate from blood instead of coelomic fluid.
d. Has a transport epithelium.