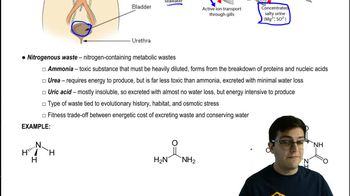
Textbook Question
Which process in the nephron is least selective?
a. Filtration
b. Reabsorption
c. Active transport
d. Secretion
1098
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Which process in the nephron is least selective?
a. Filtration
b. Reabsorption
c. Active transport
d. Secretion
Which of the following animals generally has the lowest volume of urine production?
a. Vampire bat
b. Salmon in fresh water
c. Marine bony fish
d. Freshwater flatworm
The high osmolarity of the renal medulla is maintained by all of the following except
a. Active transport of salt from the upper region of the ascending limb.
b. The spatial arrangement of juxtamedullary nephrons.
c. Diffusion of urea from the collecting duct.
d. Diffusion of salt from the descending limb of the loop of Henle.