According to the island equilibrium model, species richness would be greatest on an island that is
a. Large and remote
b. Small and remote
c. Large and close to a mainland
d. Small and close to a mainland

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


According to the island equilibrium model, species richness would be greatest on an island that is
a. Large and remote
b. Small and remote
c. Large and close to a mainland
d. Small and close to a mainland
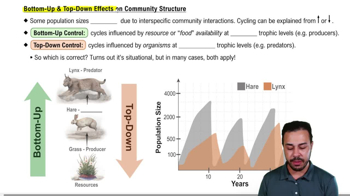
Predators that are keystone species can maintain species diversity in a community if they
a. Competitively exclude other predators
b. Prey on the community's dominant species
c. Reduce the number of disruptions in the community
d. Prey only on the least abundant species in the community
Food chains are sometimes short because
a. Only a single species of herbivore feeds on each plant species.
b. Local extinction of a species causes extinction of the other species in its food chain.
c. Most of the energy in a trophic level is lost as energy passes to the next higher level.
d. Most producers are inedible.
The most plausible hypothesis to explain why species richness is higher in tropical than in temperate regions is that
a. Tropical communities are younger.
b. Tropical regions generally have more available water and higher levels of solar radiation.
c. Higher temperatures cause more rapid speciation.
d. Diversity increases as evapotranspiration decreases.
Community 1 contains 100 individuals distributed among four species: 5A, 5B, 85C, and 5D. Community 2 contains 100 individuals distributed among three species: 30A, 40B, and 30C. Calculate the Shannon diversity (H) for each community. Which community is more diverse?