Boiling Point Elevation
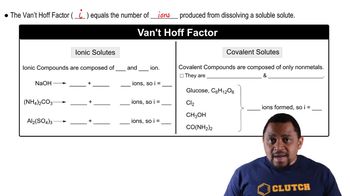
Boiling point elevation is a colligative property that describes how the boiling point of a solvent increases when a solute is dissolved in it. This phenomenon occurs because the presence of solute particles disrupts the formation of vapor above the liquid, requiring a higher temperature to reach the boiling point. The extent of boiling point elevation can be calculated using the formula ΔT_b = i * K_b * m, where 'i' is the van 't Hoff factor, 'K_b' is the ebullioscopic constant of the solvent, and 'm' is the molality of the solution.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance