Freezing Point Depression
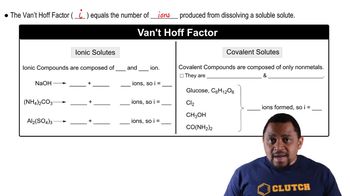
Freezing point depression is a colligative property that describes how the freezing point of a solvent decreases when a solute is added. The extent of this depression depends on the number of solute particles in the solution, which is calculated using the formula ΔTf = i * Kf * m, where ΔTf is the change in freezing point, i is the van’t Hoff factor, Kf is the freezing point depression constant, and m is the molality of the solution.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance