Textbook Question
Write balanced net ionic equations for the following reactions. Note that HClO3 is a strong acid. (a)
498
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


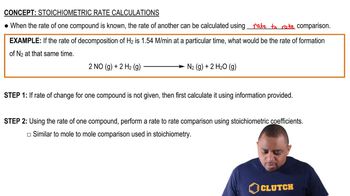
Write balanced net ionic equations for the following reactions. Note that HClO3 is a strong acid. (a)
Write balanced net ionic equations for the following reactions. Note that HClO3 is a strong acid. (b)
How many milliliters of 1.00 M KOH must be added to neutralize the following solutions? (a) A mixture of 0.240 M LiOH (25.0 mL) and 0.200 M HBr (75.0 mL)