Textbook Question
Two electromagnetic waves are represented below.
(c) Which wave represents yellow light, and which represents infrared radiation?
642
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Two electromagnetic waves are represented below.
(c) Which wave represents yellow light, and which represents infrared radiation?
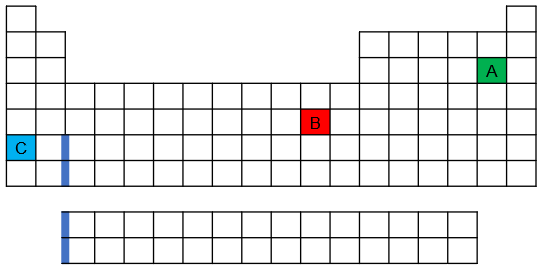
Which of the following three spheres represents a Ca atom, which an Sr atom, and which a Br atom?