Compare the control of gene regulation in eukaryotes and bacteria at the level of initiation of transcription. How do the regulatory mechanisms work? What are the similarities and differences in these two types of organisms in terms of the specific components of the regulatory mechanisms?

Explain the features of the Initiator (Inr) elements, BREs, DPEs, and MTEs of focused promoters.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Initiator (Inr) Element

TFIIB Recognition Elements (BREs)

Downstream Promoter Elements (DPEs) and Motif Ten Elements (MTEs)
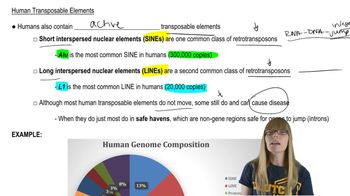
Many promoter regions contain CAAT boxes containing consensus sequences CAAT or CCAAT approximately 70 to 80 bases upstream from the transcription start site. How might one determine the influence of CAAT boxes on the transcription rate of a given gene?
Research indicates that promoters may fall into one of two classes: focused or dispersed. How do these classes differ, and which genes tend to be associated with each?
Many transcriptional activators are proteins with a DNA-binding domain (DBD) and an activation domain (AD). Explain how each domain contributes to transcriptional initiation. Would you expect repressors to also have each of these domains?
How do the ENCODE data vastly help determine which enhancers regulate which genes?
DNA supercoiling, which occurs when coiling tension is generated ahead of the replication fork, is relieved by DNA gyrase. Supercoiling may also be involved in transcription regulation. Researchers discovered that enhancers operating over a long distance (2500 bp) are dependent on DNA supercoiling, while enhancers operating over shorter distances (110 bp) are not so dependent [Liu et al. (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:14,883–14,888]. Using a diagram, suggest a way in which supercoiling may positively influence enhancer activity over long distances.
