The original source of new alleles, upon which selection operates, is mutation, a random event that occurs without regard to selectional value in the organism. Although many model organisms have been used to study mutational events in populations, some investigators have developed abiotic molecular models. Soll et al. (2006. Genetics 175: 267-275) examined one such model to study the relationship between both deleterious and advantageous mutations and population size in a ligase molecule composed of RNA (a ribozyme). Soll found that the smaller the population of molecules, the more likely it was that not only deleterious mutations but also advantageous mutations would disappear. Why would population size influence the survival of both types of mutations (deleterious and advantageous) in populations?

Recent reconstructions of evolutionary history are often dependent on assigning divergence in terms of changes in amino acid or nucleotide sequences. For example, a comparison of cytochrome c shows 10 amino acid differences between humans and dogs, 24 differences between humans and moths, and 38 differences between humans and yeast. Such data provide no information as to the absolute times of divergence for humans, dogs, moths, and yeast. How might one calibrate the molecular clock to an absolute time clock? What problems might one encounter in such a calibration?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
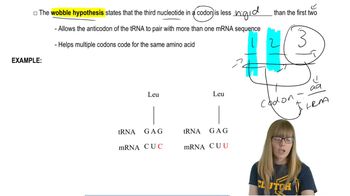
Key Concepts
Molecular Clock Hypothesis
Calibration of Molecular Clocks

Challenges in Molecular Clock Calibration

A number of comparisons of nucleotide sequences among hominids and rodents indicate that inbreeding may have occurred more often in hominid than in rodent ancestry. Bakewell et al. (2007. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. [USA] 104: 7489-7494) suggest that an ancient population bottleneck that left approximately 10,000 humans might have caused early humans to have a greater chance of genetic disease. Why would a population bottleneck influence the frequency of genetic disease?
Shown below are two homologous lengths of the alpha and beta chains of human hemoglobin. Consult a genetic code dictionary, and determine how many amino acid substitutions may have occurred as a result of a single nucleotide substitution. For any that cannot occur as a result of a single change, determine the minimal mutational distance.
Alpha: ala val ala his val asp asp met pro
Beta: gly leu ala his leu asp asn leu lys
