Suppose that base substitution mutations sufficient to eliminate the function of the operator regions listed below were to occur. For each case, describe how transcription or life cycle would be affected.
lacO mutation in E. coli

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage
Ch. 12 - Regulation of Gene Expression in Bacteria and Bacteriophage Problem 27
Problem 27 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

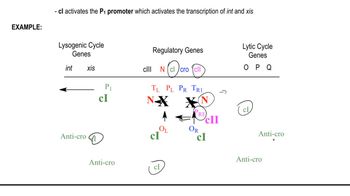

Suppose that base substitution mutations sufficient to eliminate the function of the operator regions listed below were to occur. For each case, describe how transcription or life cycle would be affected.
lacO mutation in E. coli
Suppose that base substitution mutations sufficient to eliminate the function of the operator regions listed below were to occur. For each case, describe how transcription or life cycle would be affected.
OR1 mutation in λ phage
Suppose that base substitution mutations sufficient to eliminate the function of the operator regions listed below were to occur. For each case, describe how transcription or life cycle would be affected.
OR3 mutation in λ phage
How would mutations that inactivate each of the following genes affect the determination of the lytic or lysogenic life cycle in mutated λ phage strains? Explain your answers.
cI
How would mutations that inactivate each of the following genes affect the determination of the lytic or lysogenic life cycle in mutated λ phage strains? Explain your answers.
cII
How would mutations that inactivate each of the following genes affect the determination of the lytic or lysogenic life cycle in mutated λ phage strains? Explain your answers.
cro