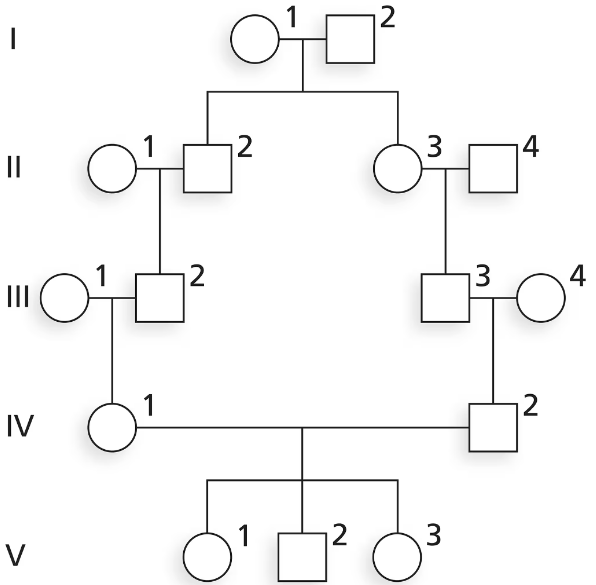
Evaluate the following pedigree, and answer the questions below for individual IV-1. What is F for this individual?

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels
Ch. 20 - Population Genetics and Evolution at the Population, Species, and Molecular Levels Problem 34c
Problem 34cEvaluate the following pedigree, and answer the questions below. Calculate F for any inbred members of this family.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Pedigree Analysis

Inbreeding Coefficient (F)

Genetic Relatedness

Evaluate the following pedigree, and answer the questions below. Which individual(s) in this family is/are inbred?
Evaluate the following pedigree, and answer the questions below. Who is/are the common ancestor(s) of the inbred individual(s)?
The following is a partial pedigree of the British royal family. The family contains several inbred individuals and a number of inbreeding pathways. Carefully evaluate the pedigree, and identify the pathways and common ancestors that produce inbred individuals A (Alice in generation IV), B (George VI in generation VI), and C (Charles in generation VIII).
Draw a separate hypothetical pedigree identifying the inbred individuals and the inbreeding pathways for each of the following inbreeding coefficients:
F=4(1/2)⁶
Draw a separate hypothetical pedigree identifying the inbred individuals and the inbreeding pathways for each of the following inbreeding coefficients:
F=2(1/2)⁵