Gene R and gene T are genetically linked. Answer the following questions concerning a dihybrid organism with the genotype Rt/rT:
If two crossover events occur between these two genes, what are the genotypes of the recombinant chromosomes?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Gene R and gene T are genetically linked. Answer the following questions concerning a dihybrid organism with the genotype Rt/rT:
If two crossover events occur between these two genes, what are the genotypes of the recombinant chromosomes?
Gene R and gene T are genetically linked. Answer the following questions concerning a dihybrid organism with the genotype Rt/rT:
Can you make a general statement about how the occurrence of two crossover events between a given pair of linked genes affects the estimate of recombination frequency?
T. H. Morgan's data on eye color and wing form genetic linkage between the two genes. Test the genetic linkage (shown in the figure below) data with chi-square analysis, and show that the results are significantly different from the expectation under the assumption of independent assortment.
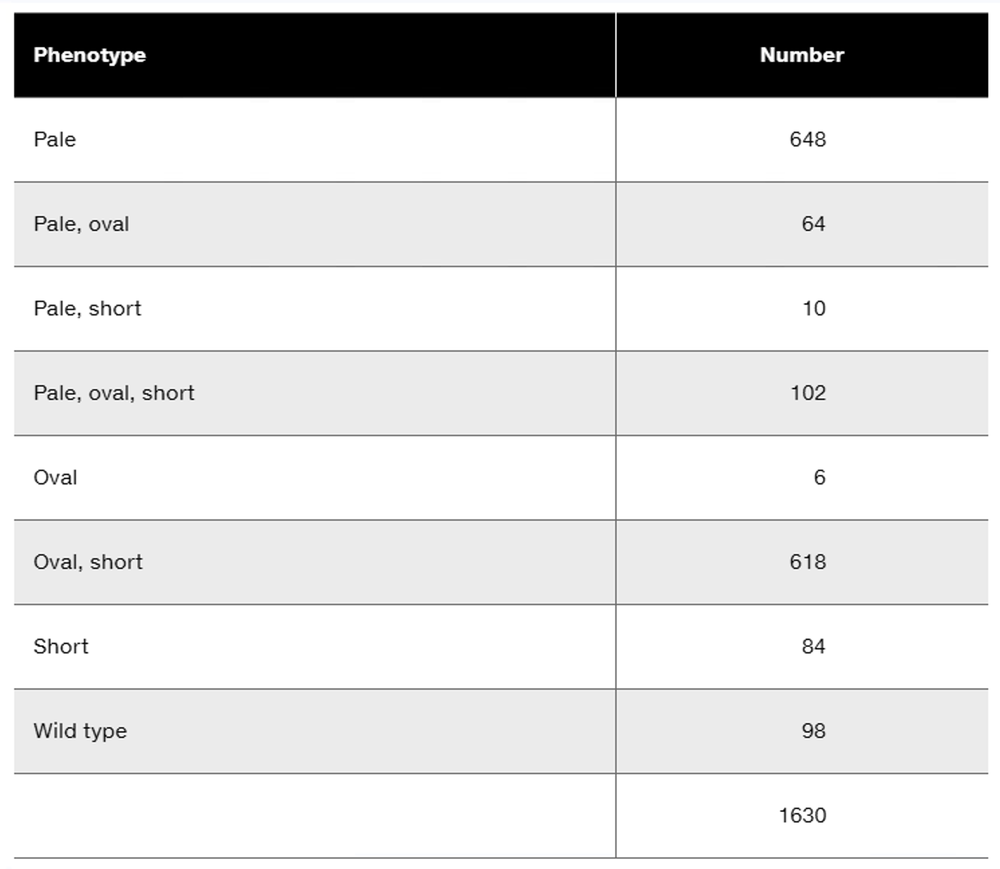
A wild-type trihybrid soybean plant is crossed to a pure-breeding soybean plant with the recessive phenotypes pale leaf (l), oval seed (r), and short height (t). The results of the three-point test cross are shown below. Traits not listed are wild type.
Calculate the recombination frequencies between the adjacent genes.
A wild-type trihybrid soybean plant is crossed to a pure-breeding soybean plant with the recessive phenotypes pale leaf (l), oval seed (r), and short height (t). The results of the three-point test cross are shown below. Traits not listed are wild type.
Calculate the interference value for these data.
The boss in your laboratory has just heard of a proposal by another laboratory that genes for eye color and the length of body bristles may be linked in Drosophila. Your lab has numerous pure-breeding stocks of Drosophila that could be used to verify or refute genetic linkage. In Drosophila, red eyes (c⁺) are dominant to brown eyes (c) and long bristles (d⁺) are dominant to short bristles (d). Your lab boss asks you to design an experiment to test the genetic linkage of eye color and bristle-length genes, and to begin by crossing a pure-breeding line homozygous for red eyes and short bristles to a pure-breeding line that has brown eyes and long bristles.
Give the genotypes of the pure-breeding parental flies and the genotype(s) and phenotype(s) of the F₁ progeny they produce.