What results from the experiments of Frederick Griffith provided the strongest support for his conclusion that a transformation factor is responsible for heredity?

Explain how the Hershey and Chase experiment identified DNA as the hereditary molecule.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
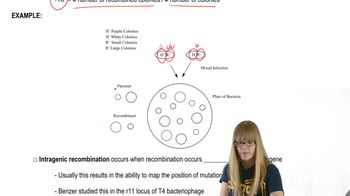
Key Concepts
Hershey and Chase Experiment

Bacteriophages
Radioactive Labeling

Explain why Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty's in vitro transformation experiment showed that DNA, but not RNA or protein, is the hereditary molecule.
Hershey and Chase selected the bacteriophage T2 for their experiment assessing the role of DNA in heredity because T2 contains protein and DNA, but not RNA. Explain why T2 was a good choice for this experiment.
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
What is the sequence of the other strand in the duplex?
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
What is the name of the bond that joins one nucleotide to another in the DNA strand?
One strand of a fragment of duplex DNA has the sequence 5'-ATCGACCTGATC-3'.
Is the bond in part (b) a covalent or a noncovalent bond?
