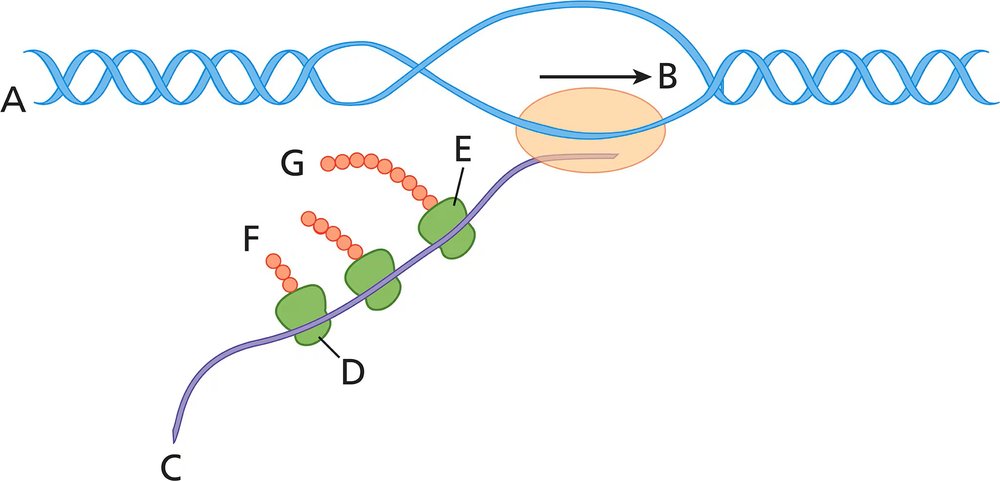
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to E? Be specific.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What structure is closest to E? Be specific.
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What name is given to the object looking like a string of beads that is closest to F?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Indicate where fMet is located in the string to the right of G.
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
What process(es) are illustrated in the diagram?
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
Does the diagram depict molecular activity in a bacterium or a eukaryote? Explain the reasoning for your answer.
For each of the following tRNA anticodon sequences, give the sequence of the corresponding codon sequence, the amino acid carried by the tRNA, and the corresponding DNA coding strand sequence and polarity.
3′-UAC-5′