Textbook Question
Identify each of the following compounds as an aldehyde or a ketone:
d.
49
views

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones Problem 18c
Problem 18c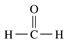
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Identify each of the following compounds as an aldehyde or a ketone:
d.
Give the common name for each of the following:
a.
Give the common name for each of the following:
b.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
b.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
c.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
d.