Textbook Question
Classify each of the following amines as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°):
c
664
views

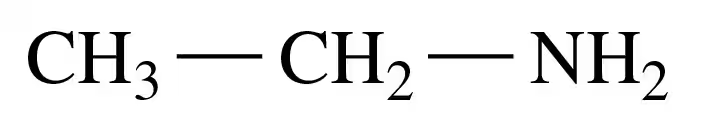
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Classify each of the following amines as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°):
c
Classify each of the following amines as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°):
d.
Classify each of the following amines as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°):
c.
Indicate if each of the following is soluble in water. Explain.
b.
Indicate if each of the following is soluble in water. Explain.
c.
Indicate if each of the following is soluble in water. Explain.
d.