After the products have formed, what happens to the enzyme?

A patient arrives in an emergency department complaining of chest pains. What enzymes would you test for in the blood serum?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Cardiac Enzymes

Troponin Testing
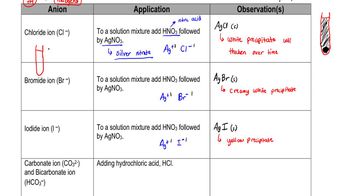
Creatine Kinase (CK) and CK-MB
What are isoenzymes?
How is the LDH isoenzyme in the heart different from the LDH isoenzyme in the liver?
Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides, functions in the small intestine at an optimum pH of 7.7 to 8.0. How is the rate of a trypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. changing the pH to 3.0
Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides, functions in the small intestine at an optimum pH of 7.7 to 8.0. How is the rate of a trypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
b. running the reaction at 75 °C
Pepsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes proteins, functions in the stomach at an optimum pH of 1.5 to 2.0. How is the rate of a pepsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. changing the pH to 5.0
