Textbook Question
Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with each of the following:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs
572
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

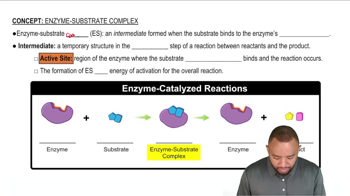

Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with each of the following:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs
Write an equation that represents an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
How is the active site different from the whole enzyme structure?
What are isoenzymes?
How is the LDH isoenzyme in the heart different from the LDH isoenzyme in the liver?
A patient arrives in an emergency department complaining of chest pains. What enzymes would you test for in the blood serum?