Write a single sentence, using no more than 25 words, to summarize each of the following cellular processes:
Translation

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


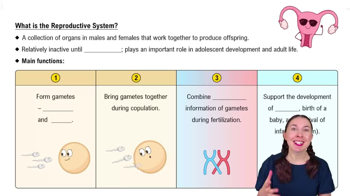
Write a single sentence, using no more than 25 words, to summarize each of the following cellular processes:
Translation
Write a single sentence, using no more than 25 words, to summarize each of the following cellular processes:
DNA synthesis
Write a single sentence, using no more than 25 words, to summarize each of the following cellular processes:
Mitosis
The three main components of a cell are the______ , the______, and the______.
What are the two fluid compartments in the body, and how are they kept separate?
Match the following terms with the correct functions.
_____Peroxisome
_____Ribosome
_____Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
_____Mitochondrion
_____Golgi apparatus
_____Lysosome
_____Rough endoplasmic reticulum
_____Vesicle
a. Modifies and folds proteins into the correct structure
b. Modifies, packages, and sorts proteins
c. Contains digestive enzymes
d. Granular organelle that makes proteins
e. Synthesizes most of a cell's ATP
f. Contains enzymes that oxidize toxins and fatty acids
g. Membrane-enclosed structure used to transport substances through the cell
h. Detoxifies certain chemicals, makes lipids, stores calcium ions