Explain why the northern United States experiences a cold season in winter and a warm season in summer?

Areas of low solar irradiation are
a. Closer to the equator than to the poles
b. Closer to the poles than the equator
c. At high altitudes
d. Close to large bodies of water
e. More than one of the above is correct
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
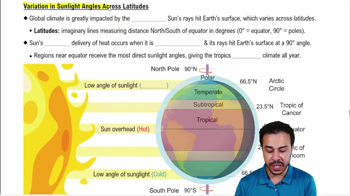
Solar Irradiation

Latitude and Climate
Altitude and Solar Exposure
An ecological footprint
a. Is the position an individual holds in the ecological food chain
b. Estimates the total land area required to support a particular person or human population
c. Is equal to the size of a human population
d. Helps determine the most appropriate wastewater treatment plan for a community
e. Is often smaller than the actual land footprint of residences in a city
The solar equator, the region of Earth where the sun is directly overhead, moves from 23.5°N to 23.5°S latitudes and back over the course of a year. Why?
a. Earth wobbles on its axis during the year
b. The position of the poles changes by this amount annually
c. Earth's axis is 23.5° from perpendicular to the rays of the sun
d. Earth moves 23.5° toward the sun in summer and 23.5° away from the sun in winter
e. Ocean currents carry heat from the tropical ocean north in summer and south in winter
Which of the following biomes is most common on Earth's land surface?
a. Chaparral
b. Desert
c. Temperate forest
d. Tundra
e. Boreal forest
Tundra is found
a. Where average temperatures are low and growing seasons are short
b. Near the poles
c. At high altitudes
d. A and B are correct
e. A, B, and C are correct
