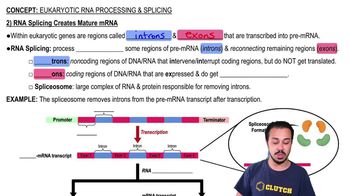
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until
a. The two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter.
b. Several transcription factors have bound to the promoter.
c. The 5′ caps are removed from the mRNA.
d. The DNA introns are removed from the template.