Using Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, calculate the uncertainty in the position of (a) a 1.50-mg mosquito moving at a speed of 1.40 m/s if the speed is known to within {0.01 m/s;

(a) For n = 4, what are the possible values of l?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
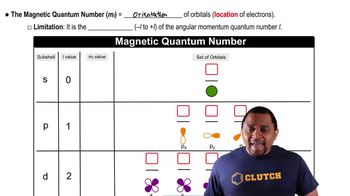
Quantum Numbers

Principal Quantum Number (n)

Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
Using Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, calculate the uncertainty in the position of (b) a proton moving at a speed of 15.00 { 0.012 * 104 m/s. (The mass of a proton is given in the table of fundamental constants in the inside cover of the text.)
Calculate the uncertainty in the position of (a) an electron moving at a speed of 13.00 ± 0.012 × 105 m/s (b) a neutron moving at this same speed. (The masses of an electron and a neutron are given in the table of fundamental constants in the inside cover of the text.)
How many unique combinations of the quantum numbers l and ml are there when (a) n = 1 (b) n = 5?
Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (a) 3p (b) 2s (c) 4f
Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (d) 5d.
