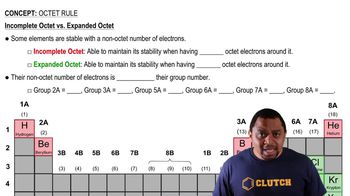
Textbook Question
For Group 13–17 elements in the third row of the periodic tableand beyond, the octet rule is often not obeyed. A friendof yours says this is because these heavier elements are morelikely to make double or triple bonds. Another friend ofyours says that this is because the heavier elements are largerand can make bonds to more than four atoms at a time.Which friend is more correct?
783
views