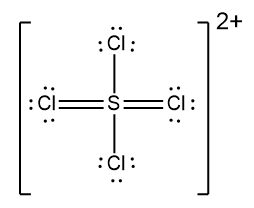
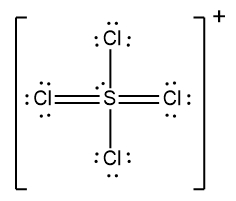
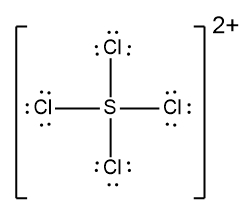
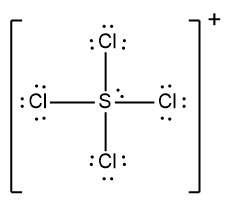
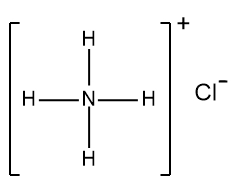
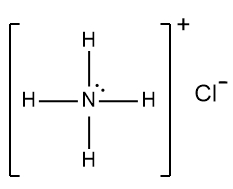
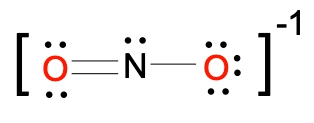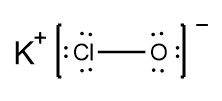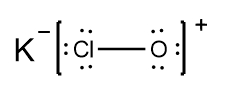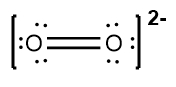In understanding ionic compounds, it's essential to recognize the differences between cations and anions. Cations result from the loss of electrons, leading to fewer valence electrons, while anions are formed by gaining electrons, resulting in more valence electrons. This concept is crucial when drawing Lewis dot structures, which visually represent the arrangement of electrons in a molecule or ion.
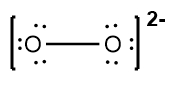
To illustrate this, consider the nitride ion (NO2-). The first step in constructing its Lewis dot structure is to calculate the total number of valence electrons. Nitrogen, located in group 5A, contributes 5 valence electrons, and each of the two oxygen atoms, found in group 6A, contributes 6 valence electrons, totaling 12 for the oxygens. Additionally, the negative charge indicates the presence of one extra electron, bringing the total to 18 valence electrons.
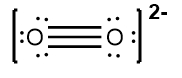
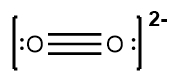
Next, place the least electronegative atom, nitrogen, at the center and connect it to the surrounding oxygen atoms with single bonds. Each bond uses 2 valence electrons, consuming 4 electrons in total. Following the octet rule, distribute the remaining electrons to ensure that each surrounding atom has 8 electrons. After placing 16 electrons, 2 remain, which are added to the nitrogen atom. However, nitrogen only has 6 electrons around it, necessitating the formation of double bonds with one of the oxygen atoms to satisfy the octet rule for all involved atoms.
To confirm the accuracy of the Lewis structure, calculate the formal charge of the nitrogen atom. The formula for formal charge is given by:
Formal Charge = (Group Number) - (Bonds) - (Nonbonding Electrons)
For nitrogen, this translates to:
Formal Charge = 5 - 3 - 2 = 0
Thus, the formal charge of nitrogen in the nitride ion is 0. Finally, since this is an ion, the entire structure should be enclosed in brackets with the charge indicated in the upper right corner, completing the representation of the nitride ion's Lewis dot structure.