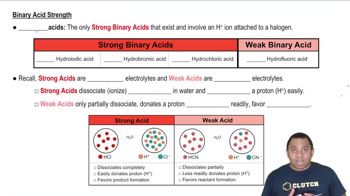
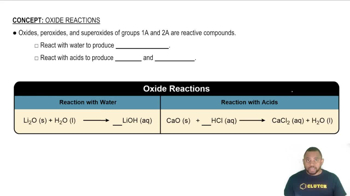
Conjugate Base Stability
The stability of a conjugate base is crucial in determining the strength of its corresponding acid. A more stable conjugate base results from factors such as resonance, electronegativity, and size of the atoms involved. In the case of H₂SO₄ and H₂SO₃, the conjugate base of H₂SO₄ (HSO₄⁻) is more stable than that of H₂SO₃ (HSO₃⁻), making H₂SO₄ a stronger acid.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance